Heat pumps are great devices that can be used for many purposes. Contrary to the name itself, heat pumps can actually be used to heat and cool your home. While most people think of air conditioners and fans when they hear about cooling, it is heat pumps that can do both effectively.
In certain situations, heat pumps can be everything you need all year round. But how does a heat pump work? We’ll cover this question in this article along with the question of whether you should get one or not. Many people don’t know how to describe a heat pump, and it’s hard to say how it works.
We have already learned that it can both warm and cool your home, but how does a heat pump work specifically? We’ll cover the essentials in this article. We will dissect the heat pump, analyze its parts and see where each part fits and what it does.
It’s a fairly complicated structure, but hopefully you will understand it better after reading this article and that you can decide whether you want to get one or not.
Components of a heat pump
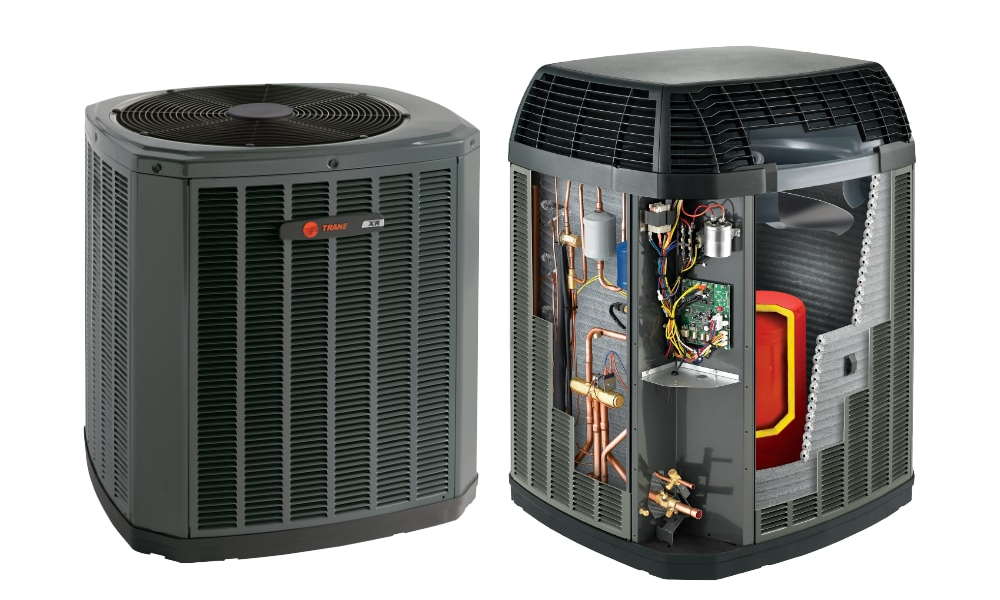
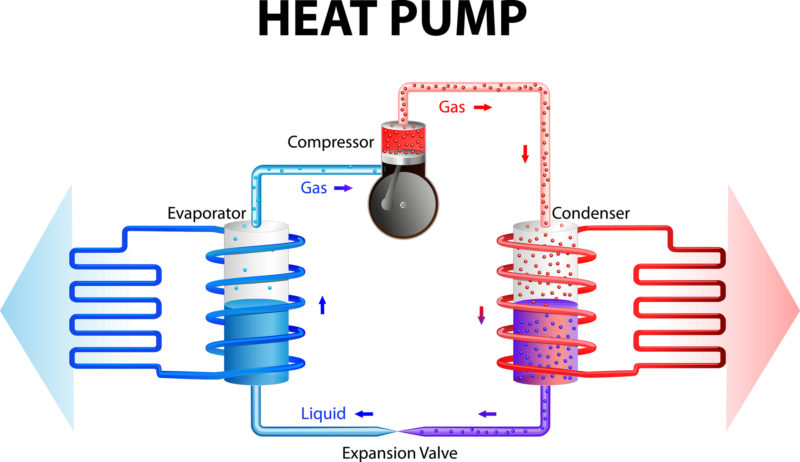
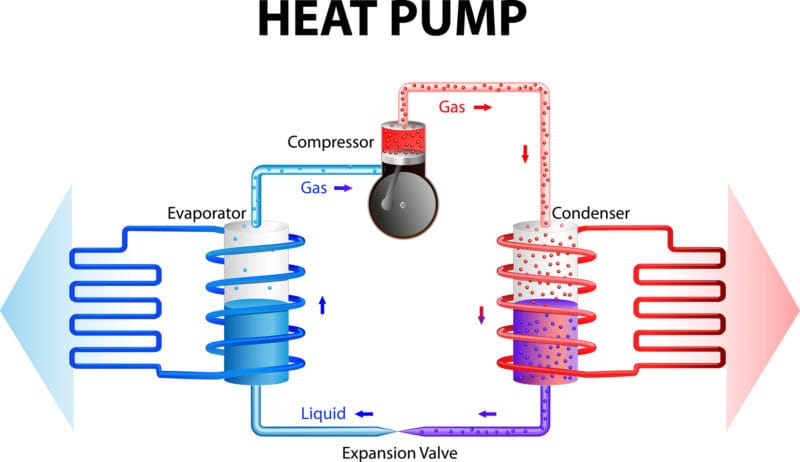
All of the heat pumps out there have two main and main components: the outdoor component, which actually resembles an outdoor component of an air conditioning system, and an indoor air conditioning component. Both components consist of many smaller parts. Let’s take a look at how a heat pump works and what components it contains.
External component
The external component is important in order to facilitate the heat exchange and so that the heat pump works properly. The outdoor unit contains a coil and a fan. The fan is used to blow air over the coil to create heat exchange.
Internal component
The internal component is the other part of the heat pump. This part of the pump also contains the coil and a fan. The coil can be used in two different ways: it can act as a condenser when the pump is in heating mode and as an evaporator when the pump is acting as a cooler. The other component of the inner component, the fan, is used to convey the air into the ducts via the coil.
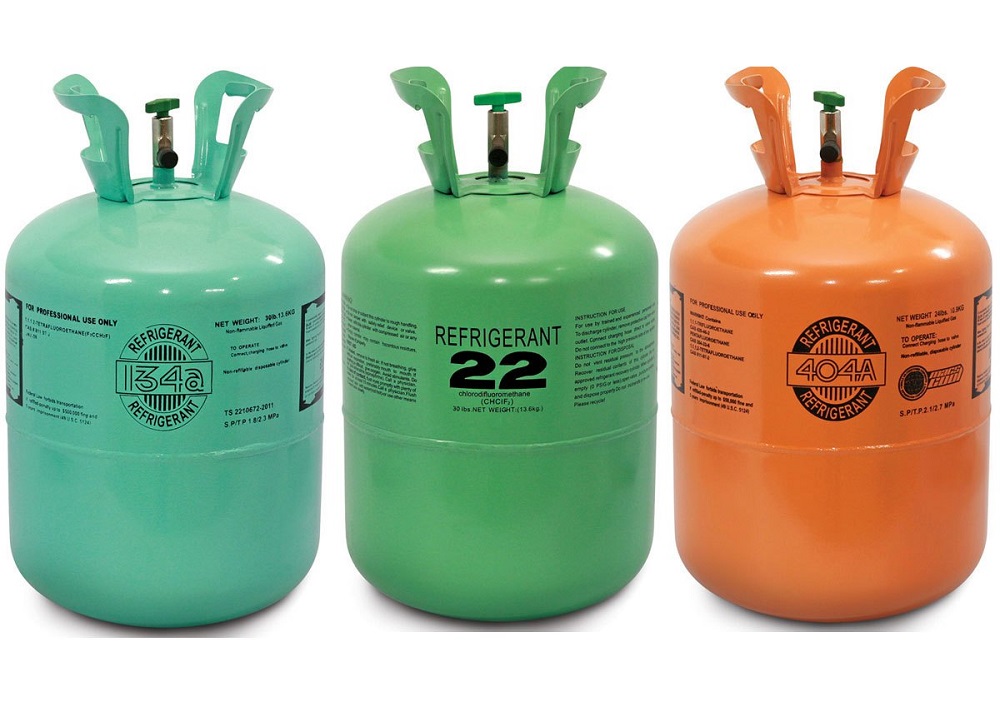
Refrigerant
The refrigerant is an important part of the heat pump because it absorbs and regulates the heat coming through the pump system.
The compressor
The compressor is used to pressurize the refrigerant and move air through the system.
Reversing and expansion valve
The changeover valve is important to regulate and reverse the refrigerant flow. This is important so that the system can switch between heating and cooling mode. The expansion valve, on the other hand, acts as a regulator, which makes it possible to reduce the pressure of the system and also to regulate the temperature.
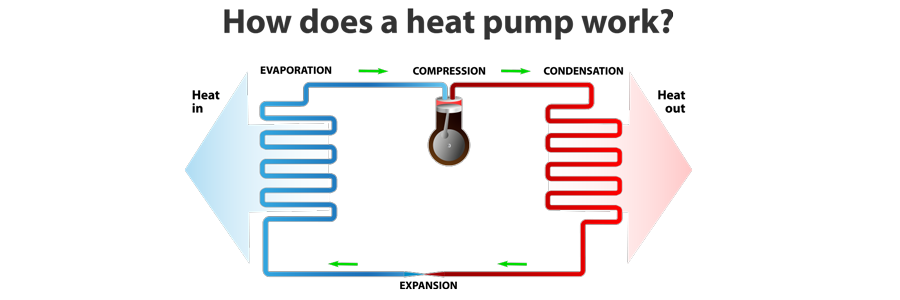
How does a heat pump work?
After getting to know all the components of the heat pump, let’s look at the important question of the article: How does a heat pump work?
We have already found that a heat pump can act as a cooler and heater. For this purpose, it has some unique and important functions. A great thing about heat pumps that makes them so popular is the fact that they are very efficient, especially more efficient than other systems that only serve as a source of heat or cold.
A heat pump uses the outside air to generate warm air. For example, it extracts heat from the cold outside air to generate heat. This is a great feature that can save you a lot of money.
Warmth is also present in cold air. A heat pump works by moving hot air from one area to another to make the most of the cold air and the conditions in which it works. It has a mechanical cooling system with a compression cycle that moves intelligently from heating and cooling cycles as required. It has an intelligent system that transports air from areas where it is not needed to areas where it is needed.
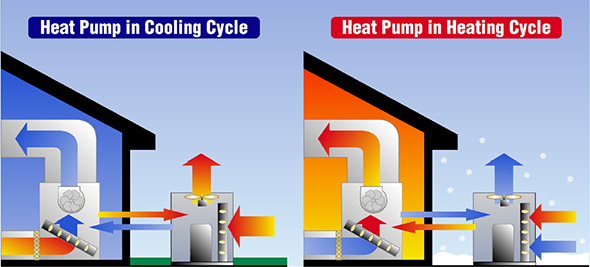
How does a heat pump work in cooling mode?
A heat pump is an efficient system that cools the area while keeping humidity low. This system is very helpful in summer and can replace air conditioning.
First, the heat pump sucks the hot air through the duct into the pump. At the same time, the compressor works hard to circulate the refrigerant between the indoor evaporator and the outdoor units. This helps the hot air move to the refrigerant, where it is cooled.
The refrigerant helps the air move from the outer condenser coil to the inner evaporator coil. This is the phase in which the air is cooled and dehumidified – this is done in the refrigerator. The cooled air is then transported to the house through the ventilation slots. This cycle continues until the desired temperature is reached.
How does a heat pump work in heating mode?
Heat pumps are becoming increasingly popular, especially in areas where the winters are milder. However, technology is evolving faster and faster, making heat pumps more efficient in areas with harsh winters.
How does a heat pump produce warmer air?
To change the cycle from cooling to heating, the outer coil acts as an evaporator while the inner coil acts as a condenser. The refrigerant flows between the outer and inner lines and moves the air from one to the other. The system is designed to extract the heat from the cold air, which is then transported from the outer coil to the inner coil.
The refrigerant is pumped to convert the heat from the cold air, extract it and transport it from the outside to the inner coil. This warmed air is then channeled through the ventilation system into the rooms of your house, which increases the temperature. The system works in cycles until the temperature in the house is set to the desired temperature.
Why buy a heat pump?
Heat pumps are very popular because they are very efficient and can be used to cool and heat your air. This method is particularly useful in areas with a temperate climate, without really harsh winters or really hot summers.
The pump works in such a way that it uses the warmth of the cold air in winter and uses this air to warm up your house. In summer, the pump extracts warm air from your home and creates cool and dehumidified air to cool your home.
Advantages of a heat pump
They are energy efficient
This is arguably the biggest advantage of a heat pump as it is a very efficient system that can save you a lot of money in the long run. Although it is an investment from the start, the long-term benefits will certainly be worth it.
You work long hours
As already mentioned, heat pumps are very good in the long term; not only because of the lower costs due to the efficiency, but also because of the very long life of a heat pump. While the lifespan can vary, you can benefit from it for a maximum of 50 years. However, the average lifespan is 15 years.
Lower CO2 emissions
A heat pump is environmentally friendly because it works very efficiently and at the same time keeps CO2 emissions low.
They are safe and require less maintenance
A heat pump is really safe to use and requires a lot less maintenance. The pump must be checked once a year, which you can do yourself. It must be checked by a specialist every four or five years.
A good heat pump can get the best of both worlds. While they’re not much more efficient than some good air conditioners or stoves, a good thing about heat pumps is that they can do both. Heat pumps can be an investment right from the start, but they can save you a lot in the long run.
If you enjoyed reading this article about how a heat pump works, you should also read this:
 TopsDecor.com Home Decor Ideas
TopsDecor.com Home Decor Ideas